Offshore Wind in the North Sea: A Blueprint for Sustainable Site Selection

The Importance of the North Sea for Wind Energy
The North Sea holds a critical position in Europe’s energy transition. The area’s favorable wind conditions and accessibility make it ideal for wind energy development, offering a significant renewable energy source to help meet climate goals. However, the North Sea is also a vibrant marine ecosystem, home to diverse habitats and species. It supports numerous human activities, including fishing, tourism, and transport, which are economically and socially vital. The high level of use demands a careful site selection process that balances energy goals with the protection of the ecosystem and the interests of local communities.
A sustainable approach to site selection benefits not only the environment and local communities but also the long-term success of offshore wind farms. By carefully evaluating sites for minimal ecological and social conflict, wind farm developers can reduce project delays and avoid costly disputes with stakeholders, such as fishing communities and conservation groups. Furthermore, sustainable site selection helps build public trust, fostering broader support for renewable energy projects. This ensures a sustainable energy transition.
Criteria for Sustainable Site Selection
Sustainable OWF site selection should consider not only technical feasibility and economic gain but also environmental and social impact, which have often been overlooked in the past.

Picture by djedj via Pixabay
Economic Criteria
Effective OWF siting contains a technical assessment of wind speed, water depth, and distance to shore to maximize energy production and minimize costs. Additionally, factors such as seabed conditions are considered to ensure economic feasibility. These criteria are essential to identify locations with optimal conditions for energy generation.
Environmental Criteria
Human activities have caused direct and indirect pressures on the North Sea by exploiting its rich productivity, resulting in a major decline in biodiversity. Criteria targeting the preservation of the North Sea’s marine biodiversity are therefore essential to take into account. Environmental criteria include proximity to marine protected areas and the potential impact on sensitive habitats and species. OWF construction and operation can affect marine life through noise, vibrations, and electromagnetic fields from cables. Special attention is given to avoiding disturbance of vulnerable species and seafloor habitats. The analysis highlights areas that balance renewable energy needs with ecological preservation, contributing to a resilient marine ecosystem.
Social Criteria
The social impact of OWFs is significant, especially for local communities and the fishing industry. Fisheries in the North Sea are economically important and are at risk of being displaced by OWFs. The selection process considers areas where these conflicts can be minimized, thereby reducing competition over fishing grounds. Addressing social concerns in site selection helps build community support and ensures that offshore wind contributes positively to local economies and social welfare. By choosing sites with lower conflict potential, OWF projects can achieve greater public acceptance and long-term sustainability.
Findings and Recommendations
The study identifies zones in the North Sea that offer high wind energy potential with minimal risk to biodiversity and limited social conflicts. In these areas, OWFs can generate clean energy without significantly impacting marine habitats or fishing industries for example.
One notable area is the Norwegian trench. If not for the technically unfeasible water depth for fixed OWFs in this trench, this area would be most suitable for sustainable offshore wind development. Floating offshore wind technologies, though in early development stages, are therefore very promising prospects, making it possible to develop wind energy in deeper waters with less impact on sensitive marine habitats.
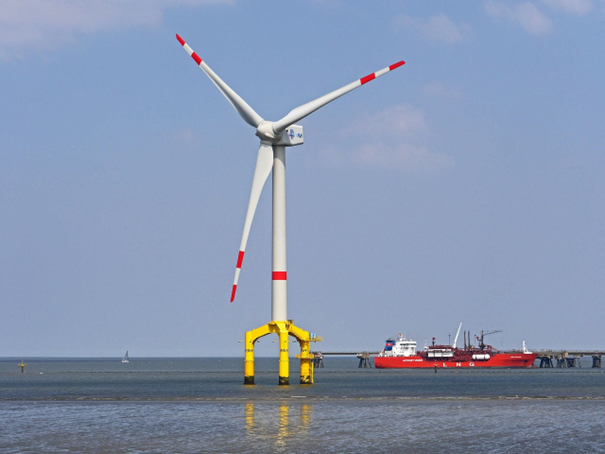

picture by hpgruesen via Pixabay
Additionally, innovations in turbine design and quieter construction techniques can help reduce disturbances to marine wildlife. As these technologies become more widely adopted, they provide valuable tools for achieving the best balance between energy production, environmental protection, and social acceptance.
In conclusion, developing OWFs in the North Sea offers a valuable pathway toward carbon-neutral energy, but it also requires careful consideration of ecological and social factors. Sustainable site selection allows offshore wind to advance climate goals while protecting marine ecosystems and local livelihoods. This study provides insights into how Europe can responsibly leverage the North Sea’s wind energy potential, fostering a future where clean energy and environmental preservation go hand in hand.